Imagine standing in the cereal aisle, comparing two boxes. One is your favorite sugary delight, and the other is a fiber-packed, vitamin-enriched option. While your taste buds may prefer the sugary pick, your body benefits far more from the extra nutrients in the healthier option.
Cybersecurity works much the same way. Raw security data on its own can be useful—but enriched data provides the crucial “nutrients” your security operations need. By adding context to raw logs and events, data enrichment helps your team detect threats more accurately, respond faster, and reduce alert fatigue.
What Is Data Enrichment?
Data enrichment enhances raw data by supplementing it with meaningful, contextual information—often pulled from external or auxiliary sources.
In cybersecurity, enrichment adds critical details to raw event logs, such as:
-
User data: Geographic location, role, access rights
-
Device information: OS versions, software profiles
-
Data classification: PII, PHI, or cardholder data (with possible redaction for privacy)
When this context is layered onto raw telemetry, your security tools can identify suspicious activity faster and with greater accuracy.
Why Data Enrichment Matters
Without enrichment, your team is forced to sift through vast amounts of ambiguous data. With it, you enable smarter, more efficient security operations by:
-
Improving threat detection: Adding threat intel to identify known indicators of compromise (IOCs) and attack patterns (TTPs)
-
Accelerating incident response: Enriched data pinpoints the root cause more quickly
-
Enhancing risk management: Context fuels more accurate anomaly detection and behavioral analytics
Example: If a user logs in from an unexpected geographic location, enriched data can help identify a potentially compromised account by correlating it with known IP risks or unusual access patterns.
Common Types of Cybersecurity Data Enrichment
Your organization already collects valuable security data—logins, network traffic, vulnerability scans, API activity, and more. But on their own, these logs may lack clarity. That’s where enrichment adds value.
Examples of enrichment sources include:
-
Threat Intelligence Feeds: Identify real-world threats using IOCs from trusted databases
-
Geolocation Data: Highlight suspicious logins from high-risk regions
-
Historical Incident Data: Helps reduce false positives through pattern recognition
-
Vulnerability Context: Links event data to known CVEs for better prioritization
3 Benefits of Enriching Cybersecurity Data
By adding more context to your security data, your security team can gain better insights into potential threats and mitigate risk more effectively.
1. Improved Threat Detection
Analytics models thrive on data. When you add context to your log data, your security analytics models gain a better understanding of the normal, baseline activity across your users and IT environment. Data enrichment also allows your security team to create high-fidelity alerts to reduce false positives.
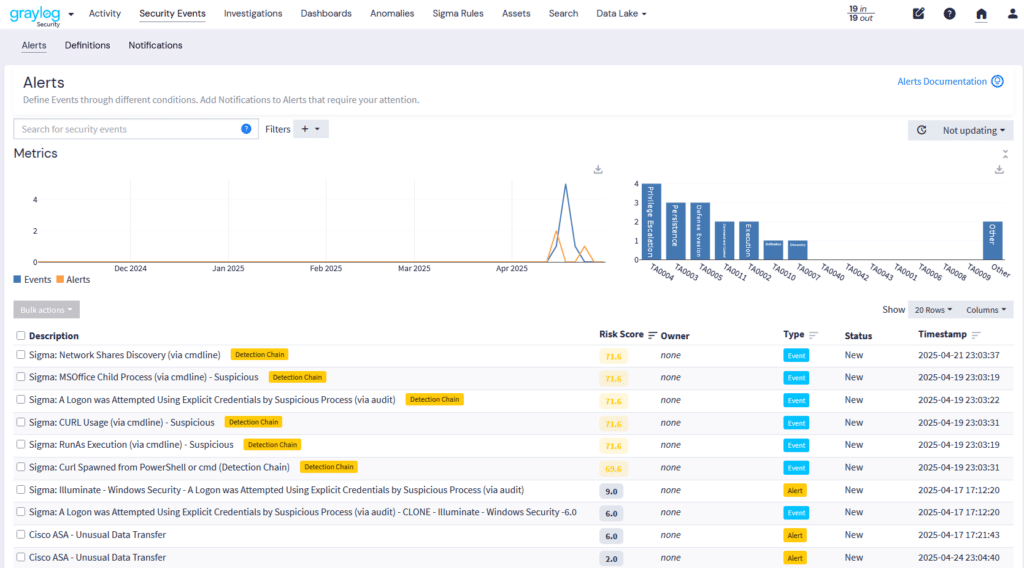
2. Improved Incident Response
Data enrichment improves key investigation and response metrics, like mean time to contain (MTTC) and mean time to resolve (MTTR). Your threat detection and incident response (TDIR) solution can use this context to help generate an incident timeline that helps your security team trace the attacker.
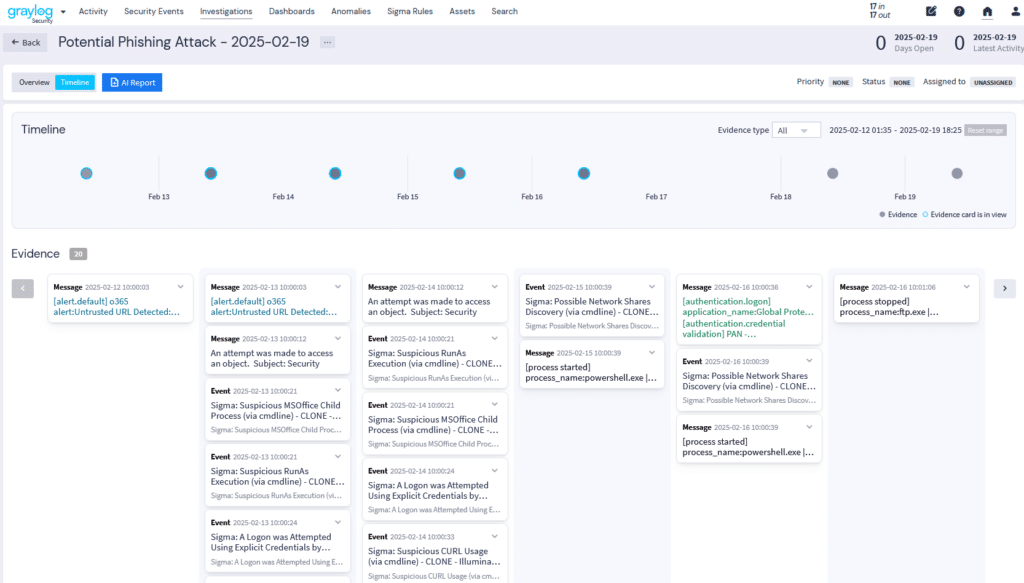
3. Reduced Storage Costs
Adding context means having all your data in a centralized location. Many organizations store their telemetry in a security data lake. When you parse and enrich the data before sending it to the data lake, you can leverage the less expensive storage solution while still having data ready for an investigation if you need it.
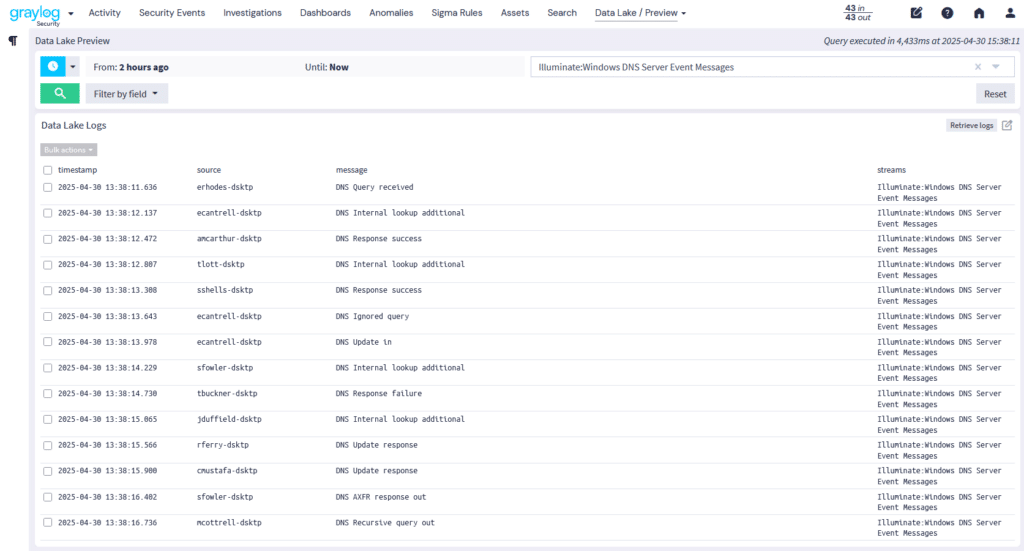
Best Practices for Enriching and Using Cybersecurity Data
Enriching cybersecurity data adds the necessary context to help your security team detect, investigate, and respond to threats more effectively. To fully harness the value of enriched data, follow these key best practices:
1. Centralize Your Security Data
The first step in any effective enrichment strategy is centralization. Consolidate log data from across your IT and security infrastructure—servers, endpoints, firewalls, cloud environments—into a single platform. This unified view allows for seamless correlation and analysis, improving threat detection and accelerating incident response.
2. Normalize and Parse Your Logs
Raw log data comes in many formats, often inconsistent and unstructured. Normalization and parsing standardize this data, extracting key information into a uniform format. This makes it easier to correlate events, identify patterns, and generate real-time insights across your environment.
3. Incorporate Threat Intelligence
Integrating external threat intelligence feeds enriches your telemetry with known indicators of compromise (IOCs) and attack behaviors. This empowers your detection systems to spot threats earlier and reduces false positives—leading to fewer noisy alerts and more actionable signals.
4. Enrich Data Before It’s Stored
If you’re using a data lake or similar storage solution, enrich and structure your data before storing it. Doing so ensures that when you retrieve logs for investigation, they’re already parsed, normalized, and context-rich—ready for quick analysis without extra processing overhead.
5. Simplify and Segment Your Data Handling
Not all data needs to be treated equally. To make enrichment more efficient:
-
Active Data: Used in real-time for dashboards, alerts, and live threat detection.
-
Warm Data: Accessed occasionally for root-cause analysis or performance monitoring.
-
Archive Data: Retained long-term for compliance, audit, or historical trend analysis.
A data management strategy helps you store, access, and enrich the right data at the right time.
6. Use Analytics to Spot Anomalies
Once data is enriched, apply advanced analytics to uncover unusual behavior—especially important in today’s distributed, hybrid work environments. Analytics tools can baseline “normal” behavior by analyzing access patterns, user roles, locations, and more. This makes it easier to detect credential misuse, insider threats, or anomalous activity before damage is done.
Graylog: Built for Enriched Security Data
Graylog’s built-in data enrichment capabilities help you transform raw logs into meaningful intelligence. Whether it’s user identity, location data, or device details, Graylog embeds this context during parsing and normalization—ensuring your data is always ready for use, no matter where it’s stored.
With enriched data in Graylog, you gain:
-
Improved risk scoring
-
Faster, more intuitive searches
-
Enhanced data visualization
-
Comprehensive insight into system health and threats
Conclusion:
Effective cybersecurity starts with enriched data. By centralizing, structuring, and contextualizing your security information, you give your team the visibility and intelligence needed to stay one step ahead of threats.
About DT Asia
DT Asia began in 2007 with a clear mission to build the market entry for various pioneering IT security solutions from the US, Europe and Israel.
Today, DT Asia is a regional, value-added distributor of cybersecurity solutions providing cutting-edge technologies to key government organisations and top private sector clients including global banks and Fortune 500 companies. We have offices and partners around the Asia Pacific to better understand the markets and deliver localised solutions.
How we help
If you need to know more about The Value of Data Enrichment in Cybersecurity Data, you’re in the right place, we’re here to help! DTA is Graylog’s distributor, especially in Singapore and Asia, our technicians have deep experience on the product and relevant technologies you can always trust, we provide this product’s turnkey solutions, including consultation, deployment, and maintenance service.
Click here and here and here to know more: https://dtasiagroup.com/graylog/