Data replication đã chuyển từ “có thì tốt” trở thành “xu thế chủ đạo” cho các trường hợp sử dụng như Tính khả dụng cao (High Availability) và khả năng phục hồi (Disaster Recovery). Đồng thời, các công ty nhận thấy nhu cầu sao chép hoặc di chuyển dữ liệu vì nhiểu lý do khác, bao gồm hiệu suất và chuyển đổi các transactional data thành các event .
Data replication là gì?
Data replication là quá trình cập nhật các bản sao dữ liệu tại nhiều địa điểm khác nhau. Mục tiêu của việc này là giữ cho dữ liệu của bạn luôn sẵn sàng khi có người cần sử dụng dữ liệu để đưa ra quyết định và cả những khách hàng đang cần để thực hiện giao dịch.
Data replication hoạt động như thế nào?
Tùy thuộc vào từng chiến lược data replication cụ thể, cơ sở dữ liệu đích của bạn có thể giống với nguồn (sao chép toàn bộ cơ sở dữ liệu – full-database replication) có thể là một phâng của nguồn (partial replication). Nếu mục tiêu của bạn là tính khả dụng cao (high availability) hoặc khả năng phục hồi (disaster recovery) thì việc duy trì các bản sao đầy đủ là điều hợp lý. Để phân tích, báo cáo hoặc theo dõi, bạn có thể giảm khối lượng công việc trên cơ sở dữ liệu nguồn bằng cách sao chép các tập hợp con, theo khu vực, chức năng kinh doanh hoặc event, của dữ liệu từ nguồn đến nhiều đích khác nhau.
Các bản sao dữ liệu cần thiết cho việc sao chép có thể được thực hiện theo nhiều cách khác nhau.
Đơn giản nhất trong số này là ảnh chụp hoặc bản sao dữ liệu được lấy tại một thời điểm nào đó. Kiểu sao chép này thường được sử dụng để sao lưu hoặc trong trường hợp dữ liệu tại đích có thể cũ hơn dữ liệu tại nguồn. Nhược điểm của snapshot là chúng chỉ là ảnh chụp nhanh hoặc hình ảnh dữ liệu của bạn tại một thời điểm cụ thể. Nếu dữ liệu nguồn thay đổi, những thay đổi đó sẽ không được phản ánh tại đích (target) cho đến khi có bản snapshot tiếp theo. Ngoài ra, snapshot thường được chụp trên toàn bộ cơ sở dữ liệu, việc này có thể tốn thời gian.
Một kỹ thuật khác đôi khi được sử dụng cho việc sao chép là sao chép hợp nhất (merge replication). Merge replication liên quan đến việc ghi lại các thay đổi được thực hiện tại nguồn và sau đó áp dụng những thay đổi đó dưới dạng một lô (batch) vào đích. Vì dữ liệu phải được xử lý nhiều lần, nên có thể xảy ra các vấn đề hiệu suất với merge replication.
Hình thức sao chép phổ biến nhất được sử dụng hiện nay là sao chép giao dịch (transactional replication). Trong hình thức sao chép này, các thay đổi hoặc giao dịch được áp dụng vào nguồn được ghi lại và sau đó được áp dụng vào đích. Transactional replication có thể áp dụng các thay đổi từ nguồn đến đích gần như trong thời gian thực, hầu hết thời gian chờ đợi là thời gian dữ liệu di chuyển từ nguồn đến đích. Điều này giải quyết các thách thức về độ trễ so với cách thức snapshot hoặc merge replication.
Lợi ích của data replication là gì?
Bạn sẽ phải ngạc nhiên về lợi ích của việc lưu trữ dữ liệu ở nhiều nơi cùng một lúc.
Đây là một lợi ích khác: dành cho các dự án tích hợp dữ liệu. Khi bạn tập hợp một lượng lớn dữ liệu từ nhiều nguồn, việc gửi dữ liệu từ tất cả các nguồn đó đến đích sao chép (replication target) sẽ giúp dữ liệu sản xuất (production data) luôn sẵn có. Trong khi đó, các công cụ tích hợp tổng hợp dữ liệu từ các kho lưu trữ khác nhau và cung cấp dữ liệu đó cho các hoạt động và việc phân tích.
“Being data-driven” có nghĩa là loại bỏ càng nhiều rào cản giữa người dùng và cơ sở dữ liệu càng tốt. Data replication là một bước tiến lớn hướng tới việc đưa dữ liệu của bạn đến nhiều nơi mà người dùng cần.
Ví dụ về data replication
Doanh nghiệp của bạn càng phụ thuộc nhiều vào dữ liệu, việc đảm bảo không có một điểm lỗi đơn lẻ (single point of failure) càng trở nên quan trọng. Khi bạn sao chép dữ liệu của mình đến các đích ở các thành phố khác hoặc múi giờ khác, bạn giúp người dùng và khách hàng của mình trong việc đảm bảo rằng họ luôn có thể truy cập vào nó.
- Các quản trị viên CNTT thường chuyển sang data để phục hồi sau thảm họa. Với dữ liệu của họ được duy trì an toàn ở hai hoặc ba địa điểm khác nhau, họ ít bị tổn thất hơn khi kinh doanh gián đoạn trong trường hợp hệ thống bị xâm hoặc thảm họa xảy ra tại bất kỳ địa điểm nào. Và vì bản sao luôn được cập nhật nên tính liên tục trong kinh doanh chỉ là vấn đề chuyển hướng lưu lượng truy cập từ nguồn bị vô hiệu hóa (disabled source) đến trang đích (target site).
- Trong thời đại mà cơ sở khách hàng và nhóm phát triển làm việc theo giờ địa, các bản sao cơ sở dữ liệu đa dạng về mặt địa lý (geo-diverse database) giúp giữ dữ liệu gần với những người cần nó. Sao chép dữ liệu là một chiến lược hữu ích để khắc phục độ trễ mạng và cải thiện hiệu suất truy cập cục bộ.
- Phân tích thời gian thực là điều không thể thiếu để tạo nên lợi thế cạnh tranh, vì vậy, các nhà quản lý ngành kinh doanh muốn chạy các truy vấn và đưa ra quyết định dựa trên các giao dịch hiện tại (current transactions). Để giữ cho các truy vấn đó không gây gánh nặng cho nguồn, quản trị viên tạo và duy trì các bản sao để các nhà phân tích sử dụng và giảm tải công việc khỏi cơ sở dữ liệu sản xuất (production database).
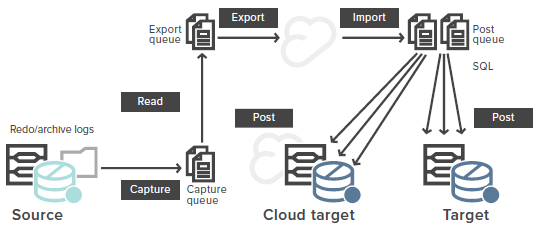
Hình ảnh dưới đây mô tả kiến trúc sao chép dựa trên nhật ký (log-based replication architecture), với dữ liệu truyền từ nguồn tới đích và cloud.
Sao chép đồng bộ và sao chép không đồng bộ (Synchronous vs. asynchronous replication)
Sao chép dữ liệu có thể đồng bộ, trong đó dữ liệu từ nhiều vị trí luôn được đồng bộ hóa và một thay đổi không được coi là hoàn tất cho đến khi nó được thực hiện xong trên cả nguồn và đích; hoặc không đồng bộ, khi các thay đổi đối với nguồn và đích là độc lập và các thay đổi đối với đích có thể bị trì hoãn.
Thông thường, việc sao chép đồng bộ sẽ tốn nhiều tài nguyên hơn và có thể dẫn đến tắc nghẽn hiệu suất. Sao chép đồng bộ thiết lập một tình huống “cam kết hai giai đoạn”, trong đó dữ liệu sẽ không được coi là sẵn sàng ở tất cả cho đến khi dữ liệu sẵn sàng ở mọi vị. Điều này có thể gây ra vấn đề về hiệu suất khi xử lý giao dịch trực tuyến hoặc các hệ thống nhạy cảm với thời gian khác. Nó cũng có thể là một vấn đề với các hệ thống nằm cách xa nhau, vì dữ liệu chưa thể di chuyển nhanh hơn tốc độ ánh sáng.
Sao chép đồng bộ thường chỉ được sử dụng khi hậu quả của việc dữ liệu không được đồng bộ hóa hoặc bị mất cao hơn chi phí liên quan. Thông thường, khi dữ liệu được ghi một lần, nó được coi là an toàn, và có thể chấp nhận một khoảng trễ ngắn giữa nguồn và đích. Với phần mềm và phần cứng tối ưu hóa ngày nay, sao chép không đồng bộ thường được chấp nhận.
Tại sao data replication lại quan trọng?
Công nghệ sao chép dữ liệu cho phép tổ chức của bạn sử dụng cơ sở dữ liệu ở hai, năm hoặc nhiều nơi cùng một lúc.
So, why is replication so important? I’ll explain how you can replicate data to your advantage in three important areas:
Vậy, tại sao sao chép dữ liệu lại quan trọng đến vậy? Tôi sẽ giải thích cho bạn lợi ích của việc sao chép dữ liệu trong ba lĩnh vực quan trọng sau:
- Phân tích và báo
- Nâng cấp và di chuyển
- Tính sẵn sàng cao và khả năng phục hồi sau thảm họa (High availability and disaster recover)
- Chuyển đổi giao dịch thành sự kiện (Translate transactions into event)
Phân tích và báo cáo
Bạn nói: “Sao chép không phải là vấn đề lớn”. “Tôi có thể gửi một tệp dữ liệu qua email cho 20 người. Sau đó, tôi sẽ có dữ liệu của mình ở 20 nơi cùng lúc.”
Đúng. Nhưng điều gì sẽ xảy ra nếu đó là dữ liệu bán hàng luôn thay đổi từ trang thương mại điện tử của bạn hoặc dữ liệu thời gian thực dựa trên phương tiện truyền thông của công ty bạn? Vào thời điểm người nhận mở tệp dữ liệu và bắt đầu phân tích, họ sẽ làm việc với dữ liệu cũ. Điều này giống như đọc một tờ báo giấy: Họ nghiên cứu dữ liệu trong tệp càng lâu thì dữ liệu càng ít được cập nhật. Bạn sẽ phải gửi tệp cập nhật mỗi khi có giao dịch mới hoặc giao dịch bị thay đổi.
Bên cạnh đó, việc gửi một tệp dữ liệu không phải là một phương pháp có khả năng mở rộng tốt. Nó có thể hoạt động với bảng tính 100KB hoặc 700KB chứa đầy dữ liệu, nhưng cơ sở dữ liệu 500GB thì sao? Bạn không thể gửi nó đi mỗi giờ.
“Trong trường hợp đó,” bạn nói, “tôi sẽ cho phép mọi người đăng nhập và truy vấn production database. Sau đó, tất cả chúng tôi sẽ truy vấn và phân tích chính xác cùng một dữ liệu tại cùng một thời điểm.”
Vâng, bằng cách đó sẽ không có ai sử dụng dữ liệu cũ.
Tuy nhiên sau đó bạn sẽ phải đối mặt với vấn đề tắc nghẽn trong cơ sở dữ liệu của mình. Các báo cáo mà bạn chạy sẽ cạnh tranh với tài nguyên của máy chủ như bộ nhớ và chu kỳ CPU với các báo cáo mà tất cả các nhà phân tích khác đang chạy. Điều này có thể dẫn đến việc giảm hiệu suất và làm chậm quá trình phân tích dữ liệu. Và tất cả những báo cáo đó sẽ cạnh tranh với các transaction của những khách hàng người trả lương cho bạn và giúp công ty duy trì hoạt động kinh doanh.
Nâng cấp và di chuyển
Trong trung tâm dữ liệu, việc thực hiện các quá trình di chuyển hoặc nâng cấp là một phần không thể tránh khỏi của việc quản lý hạ tầng IT. Tuy nhiên, trong quá trình này, sự liên tục của hoạt động kinh doanh là vô cùng quan trọng. Khách hàng và người dùng mong muốn có thể truy cập dữ liệu mà không gặp bất kỳ gián đoạn nào, họ không quan tâm đến việc hệ thống đang trải qua các quá trình cải tiến hay thay đổi.
“Không vấn đề gì,” bạn nói. “Khi chúng tôi di chuyển/nâng cấp, chúng tôi có thể sao lưu cơ sở dữ liệu của mình và khôi phục chúng đến đích. Khi chúng tôi có tất cả dữ liệu ở hai nơi, chúng tôi sẽ bắt đầu quá trình di chuyển/nâng cấp. Sau đó, ngay khi hoàn thành, chúng tôi sẽ chỉ định tất cả người dùng của mình đến môi trường mới.
Nhưng còn tất cả các giao dịch đã được thay đổi và thêm vào trong thời gian chờ đợi thì sao? Bạn sẽ mất một thời gian để làm cho môi trường mới đồng bộ với môi trường cũ. Và bạn sẽ làm gì nếu gặp vấn đề ở môi trường mới? Bạn sẽ phải khôi phục mọi thứ về vị trí cũ rồi thử lại. Đó không phải là hoạt động kinh doanh liên tục – đó là sự gián đoạn và tiếp tục trong hoạt động kinh doanh.
Sao chép dữ liệu cho phép bạn duy trì bản sao chính xác, theo thời gian thực của dữ liệu sản xuất để nâng cấp và di chuyển cơ sở dữ liệu mà không gặp bất cứ rủi ro nào. Nó giữ cho nguồn và đích được đồng bộ hóa cho đến khi thử nghiệm hoàn tất, lúc đó bạn có thể tự tin chuyển người dùng sang môi trường mới đã được nâng cấp.
Tính khả dụng cao (high availability) và khả năng phục hồi (disaster recovery)
Các quản trị viên cơ sở dữ liệu chịu trách nhiệm đảm bảo các cơ sở dữ liệu hoạt động trơn tru đồng thời vẫn chú ý đến tính khả dụng cao, khả năng phục hồi và duy trì độ tin cậy 99.999% thời gian hoạt động. Thời gian ngừng hoạt động đột ngột dẫn đến sự mất mát về dịch vụ, dữ liệu, tiền bạc và khách hàng, vì vậy công việc này tập trung vào việc duy trì hiệu quả của nhiều cơ sở dữ liệu và nền tảng khác nhau. Tính khả dụng cao đảm bảo dữ liệu luôn sẵn sàng để sự dụng, và khả năng phục hồi sau là biện pháp dự phòng lớn trong trường hợp dữ liệu đột nhiên không còn sẵn sàng.
““Cơ sở dữ liệu của chúng tôi bao gồm các công cụ tích hợp sẵn để đảm bảo tính khả dụng cao,” bạn nói, “Và chúng tôi sử dụng một công cụ khác để duy trì các bản sao từ xa nhằm phục hồi sau thảm họa. Đó là cách chúng tôi giữ dữ liệu của mình ở nhiều nơi khác nhau.”
Tuy nhiên, các công cụ tích hợp sẵn thường đắt đỏ so với chức năng hạn chế mà chúng cung cấp và một số vẫn có “a single point of failure” — một cơ sở dữ liệu chung. Nếu có sự cố xảy ra với cơ sở dữ liệu đó, hệ thống của bạn sẽ bị ngừng hoạt động trong khi bạn khôi phục. Ngoài ra, một bản copy không phải là một bản sao chép thực sự. Một bản copy chỉ là một ảnh chụp nhanh (snapshot), và snapshot của cơ sở dữ liệu sẽ trở nên lỗi thời ngay khi có một giao dịch mới diễn ra.
Mặt khác, một bản sao thực sự mang lại cho bạn tính sẵn sàng cao. Sao chép có nghĩa là bạn có cơ sở dữ liệu có thể ngay lập tức thay thế cơ sở dữ liệu khác trong trường hợp xảy ra lỗi.
Với việc sao chép dữ liệu, bạn sẽ đạt được tính sẵn sàng cao và tăng cường khả năng phục hồi sau thảm họa. Bản sao cho phép bạn chuyển người dùng sang hệ thống phụ trong thời gian bảo trì hoặc ngừng hoạt động để duy trì production database của bạn. Ứng dụng của bạn không phải đợi bạn tạo bản sao của toàn bộ cơ sở dữ liệu khắc phục thảm họa, điều đó có nghĩa là bạn sẽ không bị mất các giao dịch. Thêm vào đó, sản phẩm có tính khả dụng cao phù hợp cho phép bạn sử dụng cùng một cơ sở dữ liệu cho việc phục hồi sau thảm họa, giúp bạn duy trì tính liên tục của dịch vụ mà không cần thiết lập một cơ sở dữ liệu dự phòng riêng biệt
Chuyển các transaction thành event
Trong môi trường kinh doanh chuyển động nhanh ngày nay, ngày càng có nhiều công ty chuyển sang các dịch vụ phát trực tuyến, chẳng hạn như Kafka hoặc Azure Event Hub, để theo dõi các sự kiện đang diễn ra trong thời gian thực, tại xưởng sản xuất hoặc sàn bán hàng. Bản sao có thể biến bản ghi bán hàng hoặc máy được chèn vào cơ sở dữ liệu của bạn thành một sự kiện có thể được xử lý trong thời gian thực, cho phép khách hàng thêm tiền boa hoặc máy cần được bảo trì.
Nguồn: https://blog.quest.com/data-replication-what-is-it-and-what-are-the-advantages-of-using-it/
Về DT Asia
DT Asia được thành lập năm 2007 với sứ mệnh đưa các giải pháp bảo mật CNTT tiên phong khác nhau từ Hoa Kỳ, Châu Âu và Israel gia nhập thị trường.
Hiện tại, DT Asia đã là một nhà phân phối giá trị gia tăng trong khu vực đối với các giải pháp an ninh mạng, cung cấp công nghệ tiên tiến cho các tổ chức chính phủ trọng yếu cũng như các khách hàng tư nhân lớn bao gồm các ngân hàng toàn cầu và các công ty trong danh sách Fortune 500. Với các văn phòng và đối tác rộng khắp trong khu vực Châu Á Thái Bình Dương, chúng tôi hiểu rõ hơn về thị trường và từ đó mang đến những giải pháp bản địa hóa phù hợp với từng quốc gia, từng tổ chức.










